Image Matting and Trimaps#
Image matting is a difficult task. Therefore, most of the algorithm requires some sort of annotation. The most common one is a trimap.
Trimaps#
Trimap is a one-channel map that represents the absolute background, foreground, and unknown regions of an image. It is primarily created through human annotation, although some supervised and unsupervised machine-learning solutions can be used to generate them. However, the resulting quality may not be as good as a human annotation.
Example Trimap#
Below is a sample image and a corresponding trimap.
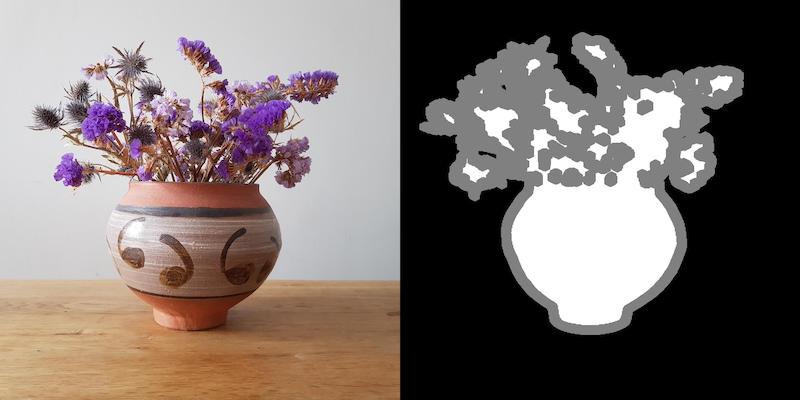

Sample Application#
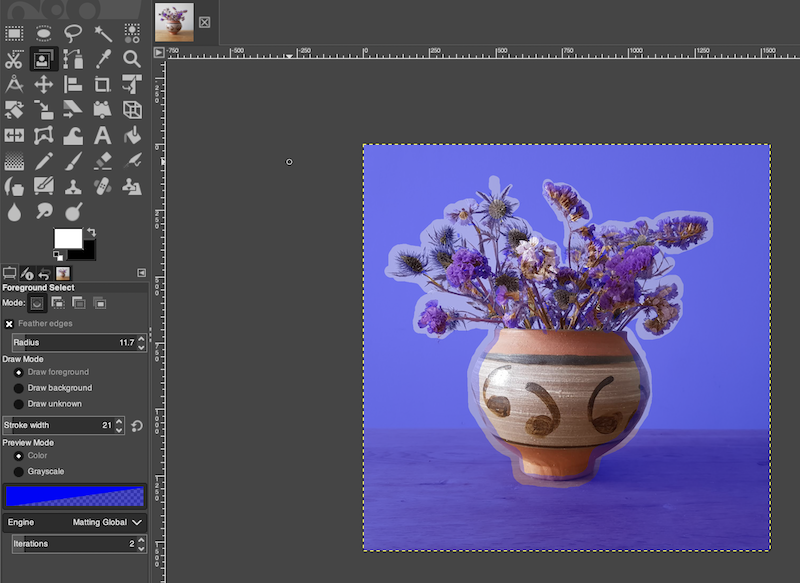
Here is the foreground selection tool interface of the GIMP image editing program.
Challenges#
An ideal trimap should contain a minimal number of unknown pixels, with clear distinctions between the foreground and background regions. It has a significant impact on the quality of the final image matting result. However, it can be challenging to create accurate trimaps due to the following reasons:
- The task may not be obvious for users in the image editing interfaces.
- Even if the user is an expert, it can be time-consuming to create a trimap.
- For some applications, trimap or other annotations may not be be feasible. For example, in real-time video processing, it is not possible to create a trimap for each frame.
Benefits#
Even though creating trimaps can be challenging, they are essential for high-quality image matting. Here are some benefits of using trimaps:
- It may improve the accuracy of the image matting process.
- Sometimes, the foreground might be subjective. For example, the user may wish to include a human but not the chair behind them. In this case, the trimap can help the algorithm to make a better decision. In other words, it provides a way to guide the algorithm to make the correct decision.
Generating Trimap From Alpha Matte#
In training machine learning algorithms, some models are designed to take the trimap as input along with the image. In this cases, it is not necessary to create a trimap manually, because it could be generated from the alpha matte through morphological operations.
This is how it works:
- First, dilate the mask to expand the regions of foreground and background pixels
- Then, erode the mask to shrink the regions of foreground and background pixels
- The resulting image will be the trimap, with the foreground and background pixels represented by white and black pixels, respectively, and the unknown pixels represented by gray pixels
Here is a function that extracts trimap from the alpha channel (Python):
Trimap Generation Function
Python function to generate a trimap from an alpha matte using OpenCV
1import numpy as np
2import cv2 as cv
3
4def generate_trimap(alpha):
5 k_size = random.choice(range(2, 5))
6 iterations = np.random.randint(5, 15)
7 kernel = cv.getStructuringElement(cv.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (k_size, k_size))
8 dilated = cv.dilate(alpha, kernel, iterations=iterations)
9 eroded = cv.erode(alpha, kernel, iterations=iterations)
10 trimap = np.zeros(alpha.shape, dtype=np.uint8)
11 trimap.fill(128)
12
13 trimap[eroded >= 255] = 255
14 trimap[dilated <= 0] = 0
15
16 return trimapMake Your Life Easier#
withoutBG API provides a simple and efficient way to remove the background from your images without the need for trimaps or other annotations. Test it out with our interactive demo below:
Drop your Image Here
or click to browse from your computer
Supports: JPG, PNG, WEBP (Max 10MB)
Try a Demo Image




